Understanding the Motorcycle Engine: Essential Knowledge for Riders
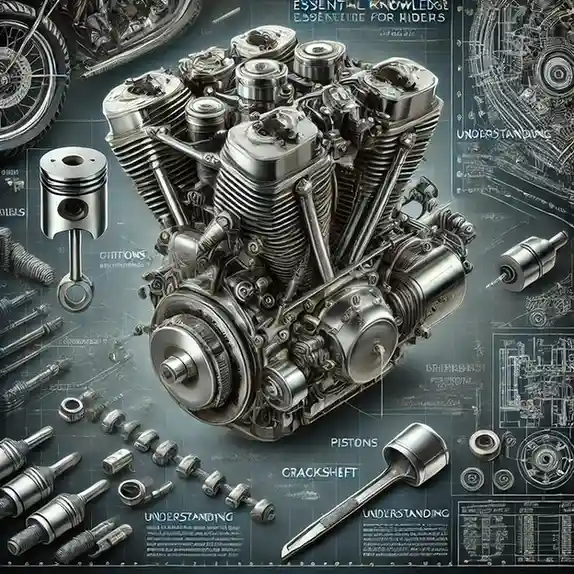

Introduction to Motorcycle Engines
The motorcycle engine is the heart of the bike, transforming fuel into the power needed to take you down the road. Understanding how your motorcycle engine works, its main components, and how to maintain it is essential for every rider. Whether you’re a seasoned biker or a new enthusiast, this knowledge can help you maximize performance, extend engine life, and enjoy a smoother, more reliable ride.
This guide covers the basics of motorcycle engines, factors influencing performance, and maintenance tips to keep your engine running at its best.
Key Motorcycle Engine Components
- Cylinder Block and Pistons
- The cylinder block houses the pistons, which move up and down to compress fuel and air. Each up-down cycle generates power through combustion, propelling the bike forward. Engines can have one to six cylinders, depending on the bike’s design, with the number of cylinders affecting power, smoothness, and torque.
- Crankshaft
- The crankshaft converts the up-and-down movement of the pistons into rotational energy that drives the bike’s wheels. This component plays a key role in engine performance, as it determines the speed at which power is delivered to the wheels.
- Camshaft and Valves
- The camshaft opens and closes the intake and exhaust valves, controlling airflow into and out of the engine. Proper timing of the camshaft is crucial to engine performance, as it ensures the right amount of fuel and air enters the cylinder for combustion.
- Fuel Injection or Carburetor
- Fuel injectors and carburetors control the mix of fuel and air that enters the engine. While carburetors are simpler and more common in older motorcycles, fuel injection systems are more precise, offering better fuel efficiency and smoother throttle response.
- Cooling System
- Air-cooled engines rely on fins that help dissipate heat, while liquid-cooled engines use a radiator and coolant to regulate temperature. Proper cooling is essential to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance.
Types of Motorcycle Engines
Motorcycles come with various engine types, each offering unique characteristics in terms of power, efficiency, and ride quality:
- Single-Cylinder Engines: Lightweight, compact, and efficient, these engines are common in smaller bikes and dirt bikes.
- Parallel-Twin Engines: Known for a good balance of power and efficiency, they’re common in commuter and touring bikes.
- V-Twin Engines: Delivering a strong low-end torque and iconic rumble, V-Twins are popular in cruiser motorcycles.
- Inline-Four Engines: Found in sportbikes, these engines offer high power output and smooth operation at higher RPMs.
- Boxer Engines: With cylinders positioned horizontally, these engines offer a low center of gravity, providing stability and balance.
Factors Influencing Motorcycle Engine Performance
1. Engine Displacement
- Displacement refers to the total volume of all cylinders in the engine, usually measured in cubic centimeters (cc). Larger displacement generally means more power and torque, translating to faster acceleration.
2. Compression Ratio
- The compression ratio is the difference between the cylinder’s volume at the bottom and top of the piston stroke. Higher compression ratios lead to more efficient fuel combustion, providing greater power but requiring higher-octane fuel.
3. RPM (Revolutions Per Minute)
- RPM measures how fast the engine is spinning. Higher RPMs mean more power, but excessive revving can strain the engine over time. Sportbikes, for example, are designed to handle higher RPMs than cruisers.
4. Fuel and Air Mixture
- The ideal air-fuel ratio is essential for smooth combustion. Proper fuel injection or carburetion provides the optimal mix, impacting both performance and fuel efficiency.
Essential Engine Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance keeps your motorcycle engine running smoothly, helping you avoid costly repairs and ensuring peak performance.
1. Check and Change Engine Oil Regularly
- Engine oil lubricates, cleans, and cools internal components. Check the oil level regularly, and follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals, typically every 3,000 to 5,000 miles.
2. Inspect the Air Filter
- A clean air filter is essential for maintaining the correct air-fuel mixture. Check and clean or replace the air filter as needed to prevent dirt from entering the engine and affecting performance.
3. Spark Plug Maintenance
- Spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder. Worn or fouled spark plugs can reduce power and fuel efficiency. Inspect and replace them according to your bike’s maintenance schedule.
4. Cooling System Care
- For liquid-cooled engines, regularly check coolant levels and replace the coolant every two years. For air-cooled engines, ensure fins are free of debris and dirt to maintain optimal airflow.
5. Regular Valve Adjustment
- Adjusting the valves ensures they open and close at the correct intervals, keeping the engine running efficiently. Some motorcycles require regular valve adjustments, while others have self-adjusting mechanisms.
6. Check the Timing Chain and Camshaft Tensioner
- The timing chain synchronizes the crankshaft and camshaft. If it becomes loose or worn, it can disrupt the engine’s timing, leading to rough performance or even engine damage.
Conclusion: Knowledge is Power for Motorcycle Engine Care
Understanding your motorcycle engine and how to maintain it is key to keeping your ride smooth, powerful, and reliable. From knowing the essential components and performance factors to following a regular maintenance schedule, taking care of your engine means more enjoyment and fewer repairs down the road. So, take the time to get familiar with your engine—knowledge is power when it comes to a well-maintained motorcycle!
Read also our article about Discovering Abia: Top Attractions & Cultural Highlights.



1 thought on “Understanding the Motorcycle Engine: Essential Knowledge for Riders”